Indexing queue
Before your users can search your Magento data, you need to upload it to Algolia’s servers in a process called indexing. The indexing queue sends updates to products, categories, pages, and other data to Algolia’s servers asynchronously. This way, the data in Magento and on Algolia’s servers is always up to date, providing the best user experience.
Because the indexing queue works asynchronously in the background, the Magento administrator doesn’t have to wait after every change.
Configuring the queue
You should enable the indexing queue in production environments.
To enable the queue, go to Stores > Configuration > Algolia Search > Indexing Queue/Cron in the Magento dashboard.
All queued operations are stored in the database, in the table algoliasearch_queue.
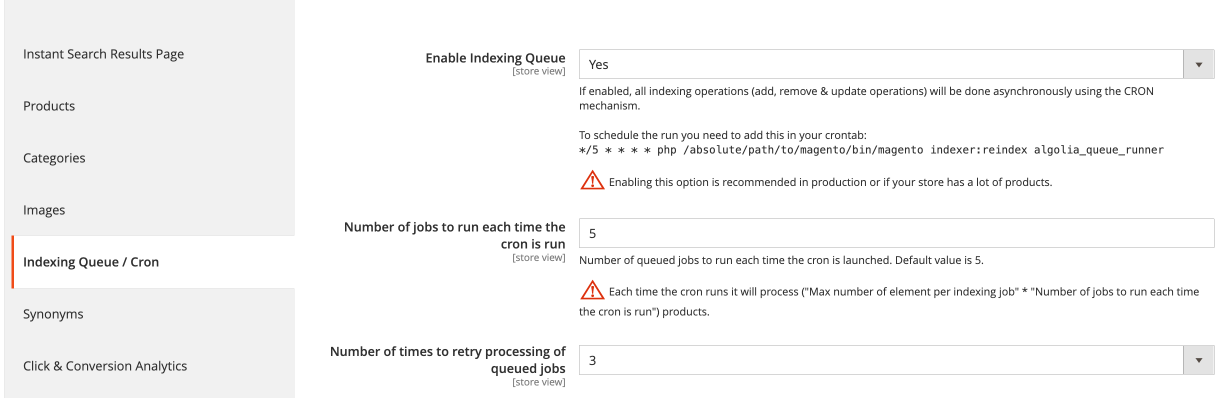
After turning on the indexing queue in Magento, you need to set up processing the queue.
By default, the queue runs up to 5 operations at the same time.
Depending on the available resources on your server, you can adjust this number
by changing the Number of jobs to run each time the cron is run setting.
To keep your data synchronized between Magento and Algolia,
the indexing queue needs to finish processing between cron intervals.
To find out how many operations the server can handle, you can try the following (this example assumes that the indexing queue runs every 5 minutes):
- Turn off the cron job.
- Set the number of operations to process to 10.
- Manually run the indexer.
- Measure how long one run takes.
- If it takes less than 4 minutes, increase the number of jobs.
- Repeat from point 3 until the indexing takes longer than 4 minutes.
- Turn the cron job back on.
It’s best practice to keep a margin in case the cron job is slower, for example, due to a high server load. That’s why the example uses 4 minutes as a threshold.
Failed operations
When an operation fails during the processing of the queue, it’s added back to the queue. To prevent operations from being added back infinitely, you can adjust the Number of times to retry processing of queued jobs setting.
Processing the queue
After enabling the queue, you need to set up a process to handle the queue.
Process the indexing queue automatically
The preferred way to handle the queue is by processing it at a regular time interval.
To do this, add the following crontab entry:
1
*/5 * * * * php absolute/path/to/magento/bin/magento indexer:reindex algolia_queue_runner
This entry processes the indexing queue every 5 minutes, running five indexing operations by default.
Process the indexing queue manually
You can trigger the indexing jobs manually:
1
php path/to/magento/bin/magento indexer:reindex algolia_queue_runner
If you manually process the indexing queue, it only runs the specified number of operations (the default is five) This may not be enough to empty the queue.
Processing the full queue (not recommended)
To process all operations and empty the indexing queue,
add the environment variable: PROCESS_FULL_QUEUE=1 to the command:
1
PROCESS_FULL_QUEUE=1 php path/to/magento/bin/magento indexer:reindex algolia_queue_runner
When processing many operations, the chances of errors increase: network timeouts, PHP timeouts, or memory issues could lead to the data in your Algolia indices not being up to date. See the troubleshooting guide if you encounter any issues.
Clearing the queue
To clear your queue, go to Stores > Algolia Search > Indexing Queue in your Magento dashboard and click Clear Queue to remove all jobs from the queue.
Additionally, you can truncate your algoliasearch_queue table in your database.
If you clear your indexing queue, you should perform a full reindexing so that your Algolia indices have up-to-date data.
Indexing queue logs
To check the performance of your indexing queue, you can review the table algoliasearch_queue_log in your database.
Each row represents one process of the algolia_queue_runner indexer, whether from the cron job or a manual run.
The duration column shows the time in seconds needed to process the indexing queue.
To account for extra processing time and server load variations,
the duration should be at least one minute shorter than your cron job interval.
For example, if you set the cron interval to 5 minutes (300 seconds),
the duration of the indexing jobs should be less than 240 seconds (4 minutes).
If you’re performing well under the recommended duration, you can increase the number of processed jobs to optimize your queue runner. You can find this setting in Stores > Configuration > Algolia Search > Indexing queue / Cron > Number of jobs to run each time the cron is run.
Likewise, if you’re performing over the recommended time, you should reduce the number of processed jobs.
To see the indexing queue logs, go to Stores > Algolia Search > Indexing Queue > See Run Logs in the Magento dashboard.
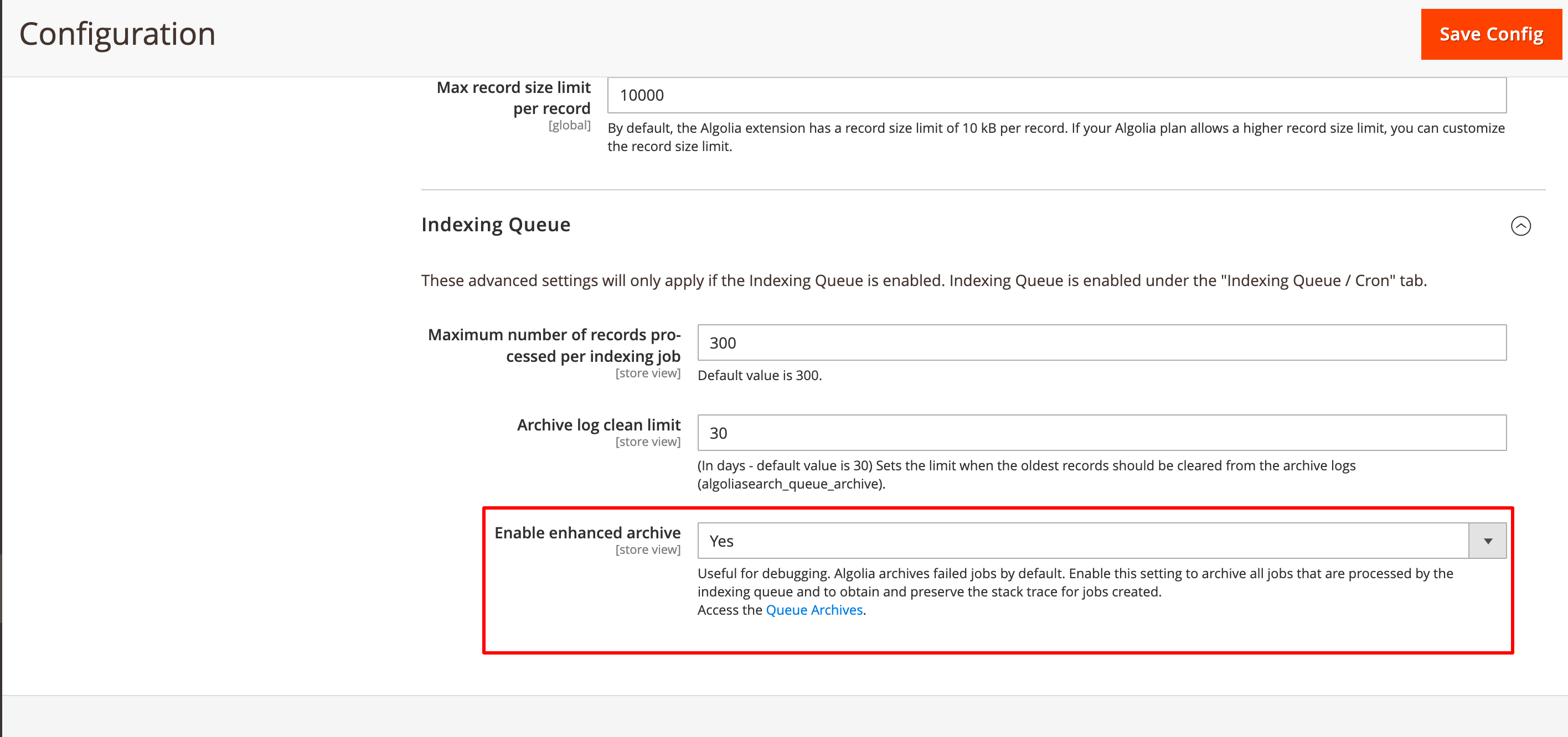
Indexing queue archives
Go to Stores > Algolia Search > Advanced > Indexing Queue in the Magento dashboard and set Enable enhanced archive to Yes to archive all jobs that are processed by the indexing queue and to obtain and preserve the stack trace for jobs created.
Indexer modes
Magento has two indexing modes:
Update on Save. When an entity updates, Magento indexes the saved event’s data.Update on Schedule. Magento bypasses these events by creating MySQL table triggers to store updated entity IDs in a change log*_cltable.
The Magento cron job indexes these IDs later.
You can set the following indexers to Update on Schedule:
| Indexer name | Indexer ID |
|---|---|
| Algolia Search Products | algolia_products |
| Algolia Search Categories | algolia_categories |
| Algolia Search Pages | algolia_pages |
Setting the Algolia Search Queue Runner algolia_queue_runner indexer to Update on Schedule isn’t recommended. In combination with the recommended cron, changing this mode to Update on Schedule can cause strange indexing behavior including data loss from concurrent job processing. For better performance, keep this indexer set to Update on Save.
